
Ali Heydari
Creating snapshots
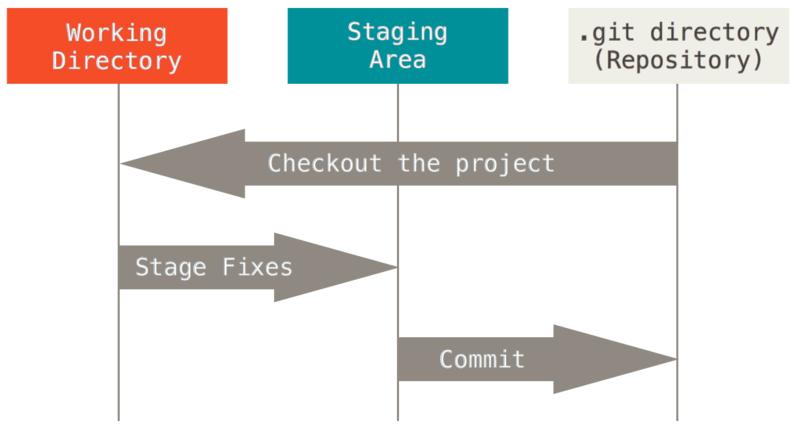
Git workflow
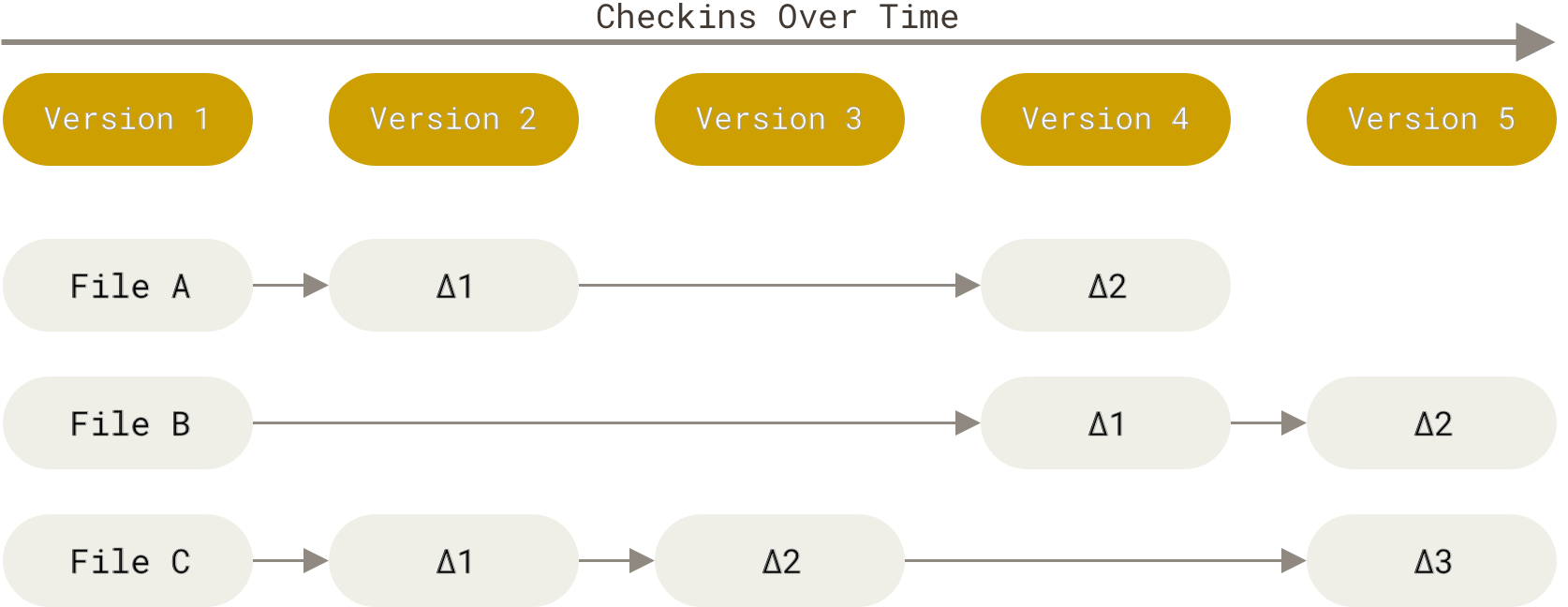
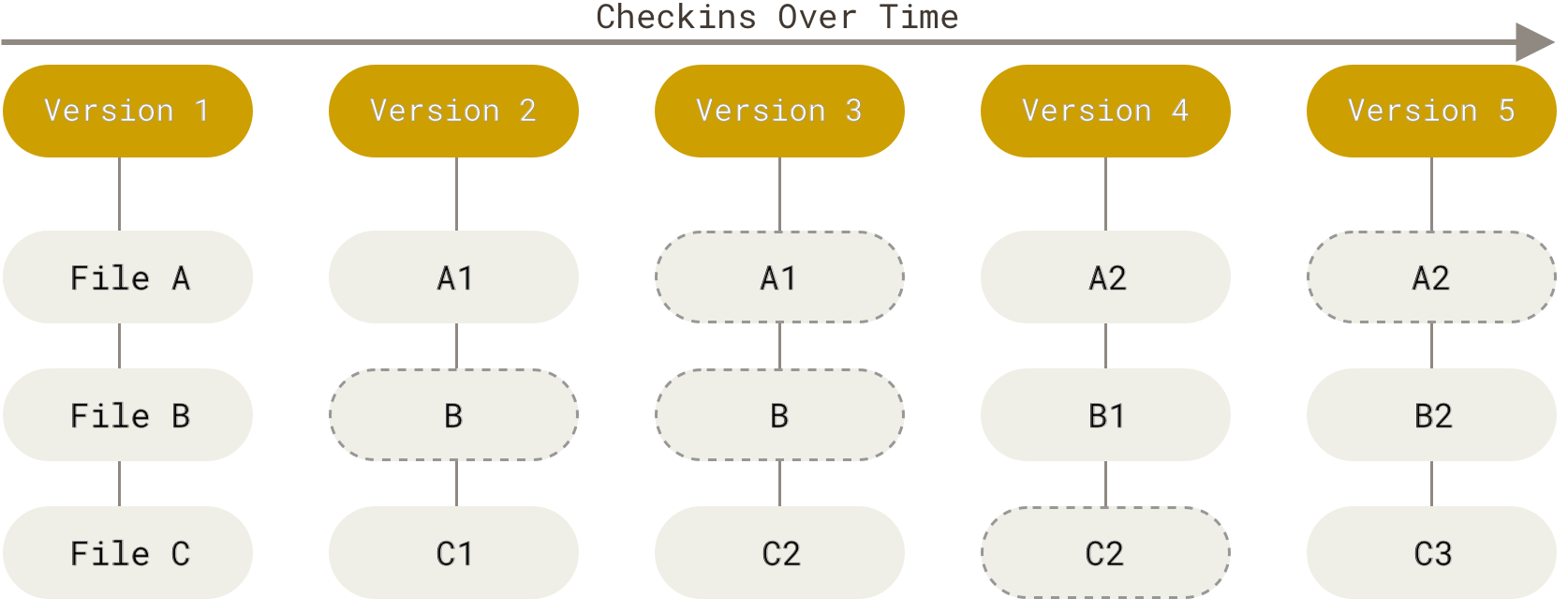
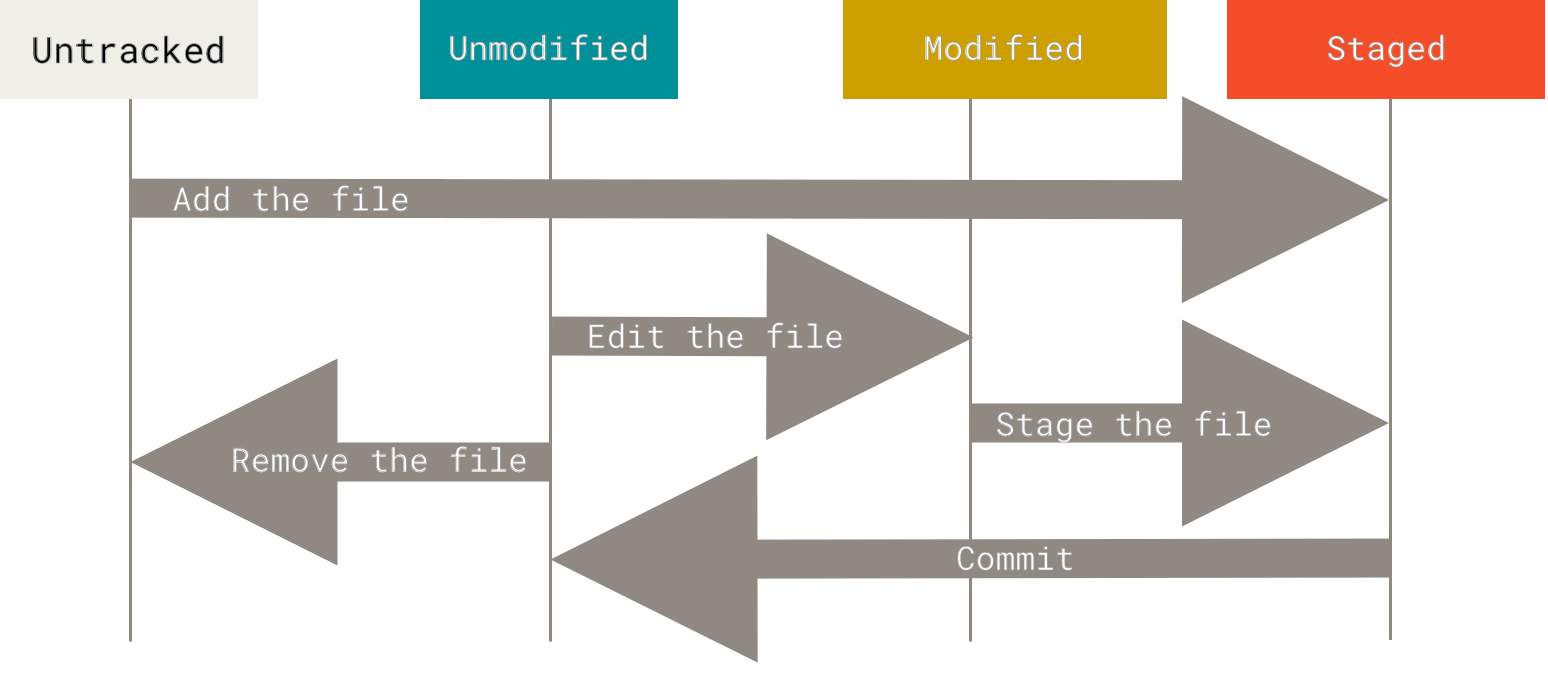
Staging files
git add
git add file1.js file2.js: adding multiple file with oneline commandgit add package*: adding files with wildcardgit add -f index.js: allow adding otherwise ignored filesgit add .: add all file in current and subdirectory recursivly.
Committing changes
git commitgit commit -m "Initial commit"
Committing best practices
links: 5 Git Best Practices For Git Commit, Conventional Commits
Skipping the staging area
git commit -a
Removing files
rmvsgit rm
using rm:
$ rm pankod-icon.svg
$ git status
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
deleted: pankod-icon.svg
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
$ git add pankod-icon.svg
$ git status
On branch main
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
deleted: pankod-icon.svg
using git rm:
$ git rm pankod-icon.svg
rm 'public/icons/pankod-icon.svg'
$ git status
On branch main
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
deleted: pankod-icon.svg
git rm packages/*git rm --cached: only remove from the indexgit ls-files
Renaming or moving files
mvvsgit mvgit mv index.js index.ts
Ignoring files
add gitignore file <gitignore.io>
$ git add .gitignoreHow can I make Git "forget" about a file that was tracked, but is now in .gitignore?
run command:
git rm --catched <file_or_directory_or_pattern>Also you can add
.gitignoreand run the following command:
git rm --cached -r . && git add . && git commit -m "track files in right way"
Short status
git status -s
left column in output represents the staging aria
right column in output represents the working directory
$ git status -s
M _markdowns/_lectures/2-creating-snapshots.md
$ git add .
$ git status -s
M _markdowns/_lectures/2-creating-snapshots.md
Viewing staged and unstaged changes
git diff --staged
meanig of git diff output
Visual diff tools
use VSCode add default diff tool:
$ git config --global diff.tool vscode
$ git config --global difftool.vscode.cmd "code --wait --diff $LOCAL $REMOTE"
see git config settings:
git config --global -e
Viewing history
git log
git log --oneline
git log --oneline --reverse
Viewing a commit
git show
git show COMMIT_SHAgit show HEADgit show HEAD^^git show HEAD~2git show HEAD~2:.gitignoregit show HEAD~2:src/index.tsgit ls-tree HEAD~3
Git objects
- commits
- blobs (files)
- trees (directories)
- tags
Unstaging files
git reset --hard
git restore
git restore --staged index.js
Discarding local changes
git restore .
git clean
git clean -fd
Restoring a file to an earlier version
git restore --source=HEAD~1 index.js
Attachments: [session video 📺](\\192.168.100.14\Training Courses\git)